TYPES OF BUYERS
TYPES OF BUYERS
Buyers can typically be broken down into three categories:
1 Entrepreneurial Buyers:
Typically an individual or small group of business people who are looking to purchase and run their own business. Their funding comes typically from real estate equity and cash they have accumulated through their efforts (employment or other business ventures). They often don’t have specific experience in the industry or market of the target company, but have the entrepreneurial drive to learn and be successfully.
Entrepreneurial Buyers approach to valuation is a balance between:
- Earning a FMV Salary for the job they do
- Ensure that the business can afford to pay the financing put in place for the acquisitions
- A risk appropriate Return on Equity that the personal equity they invested.
2 Strategic Buyer
Typically a business looking to make a strategic acquisition to complement their current operations. The strategic buyer’s motivation could be one of:
- Consolidation (eg. Buying a competitor)
- Integration (eg. buying up or down their supply chain)
- Growth (eg. buying distribution channels, customers or product/service capabilities)
The strategic buyer can often realize operational synergies and cost savings by acquiring a target company thereby improving the overall cash flow of the business. This means that their ROE would be higher than compared to an entrepreneurial buyer, and often strategic buyers are less price sensitive and tend to be willing to pay higher price.
3 Investment Buyer
Investment buyers tend to be a more sophisticated buyer who views a target company strictly based on the financial numbers. A typical investment buyer would be a Private Equity firm who is looking to make a strategic acquisition of a business from an investment and performance perspective. Key for this type of buyer would be to have a well-seasoned management team in place to continue to run the day to day operations. The Investment buyer generally does not take an active role in the running of the business, but rather takes on a director role, helping setting strategic direction and providing growth financing as needed.
Investment buyers tend only acquire a business with a clear exit strategy in place. It is not uncommon for Investment buyers to offer the seller incentives to continue in the company after the transaction with stock option or similar incentives. Investment buyers are typically highly sophisticated and disciplined, and will pay up to the ROE they expect from the acquisition based on risk, strategic benefits, etc. There is usually very little emotional influence on their decision making process. Typically these type of buyers will not look at
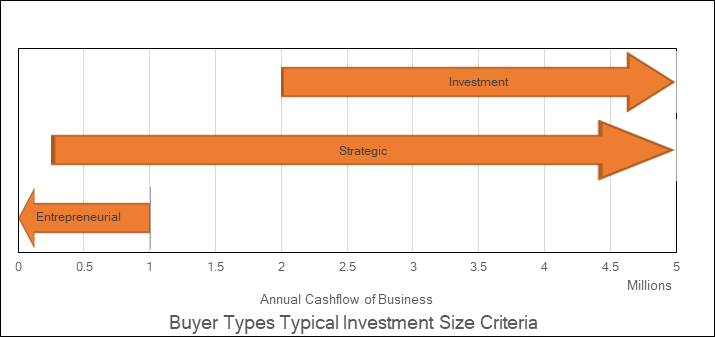
businesses under about $2 million in cash flow as the costs of acquisition is higher for the investment buyer.
